IntelliCAD has always — since its first release twenty years ago — been based on technology that is now governed and advanced by the Open Design Alliance (ODA). In the beginning the focus was on .dwg, but over the years, both technologies have seemed to outgrow their initial aim on replicating the .dwg file format (ODA) and replicating its end-user capabilities (ITC).
This point was not necessarily highlighted in Prague, but the link between ITC and ODA technology was mentioned throughout the conference with the nonchalant transparency that is commonplace among the IntelliCAD community.
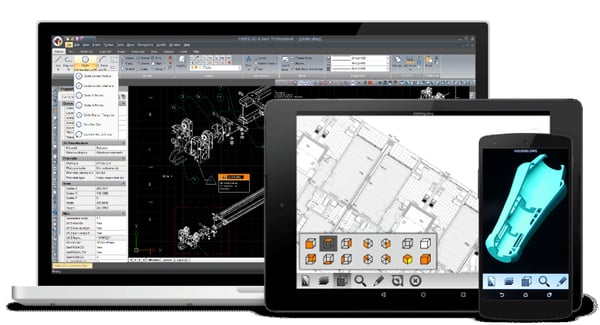
- IntelliCAD — Uses the latest ODA libraries.
- BIM — Attach Autodesk® Revit® files as underlays, based on the ODA BIM component.
- Mobile — Based on ODA libraries.
- Walls, windows, doors, slabs — Draw and edit architectural entities (new in IntelliCAD 9), based on the ODA Architecture component.
- Smart meshes — Draw and edit lightweight 3D meshes (new in IntelliCAD 9), based on the ODA Facet Modeler.
- Custom objects — Work with custom architecture, civil, and mechanical objects, based on ODA Architecture, Civil, and Mechanical components.
The ITC employs many components of ODA technology (including ODA source code), then customizes that technology according to the needs of their members. And that's exactly what ITC members do: they employ many components of ITC technology (including ITC source code), then customize that technology according to the needs of their end-users. It's a consistent business model from start to finish.
